In 2020, the overall public and private consumption of antibiotics in Italy was 17.7 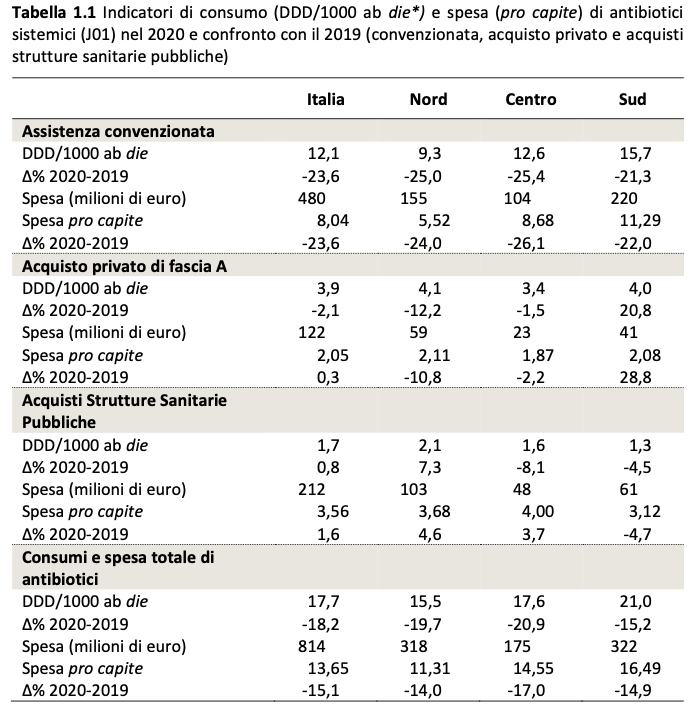 DDD/1000 inhabitants per day, a sharp reduction compared to 2019 (-18.2%) (Table 1.1).
DDD/1000 inhabitants per day, a sharp reduction compared to 2019 (-18.2%) (Table 1.1).
In 2020 antibiotics represented, with 692.1 million euros, 3.0% of expenditure and, with 13.8 DDD/1000 inhabitants per day, 1.2% of total consumption paid by the NHS (OsMed Report 2020) .
Almost 80% of the total doses (13.8 DDD/1000 inhabitants per day) were dispensed by the National Health Service (SSN), with a reduction of 21.7% compared to 2019. This figure includes both antibiotics dispensed under agreement (from public and private pharmacies) and those purchased from public health facilities.
The share of antibiotics purchased by public health facilities, compared to the resident population, represented a minor part of consumption paid by the NHS (1.7 DDD/1000 inhab day), although its monitoring is of great importance for the control of antibiotic resistance in the hospital.
Overall, consumption remains higher than in many European countries. NHS per capita expenditure (11.6 euros) decreased compared to the previous year.
Private purchases of antibiotics reimbursable by the NHS (class A) amounted to 3.9 doses per 1000 inhabitants, which correspond to 24% of the total territorial consumption of antibiotics, and 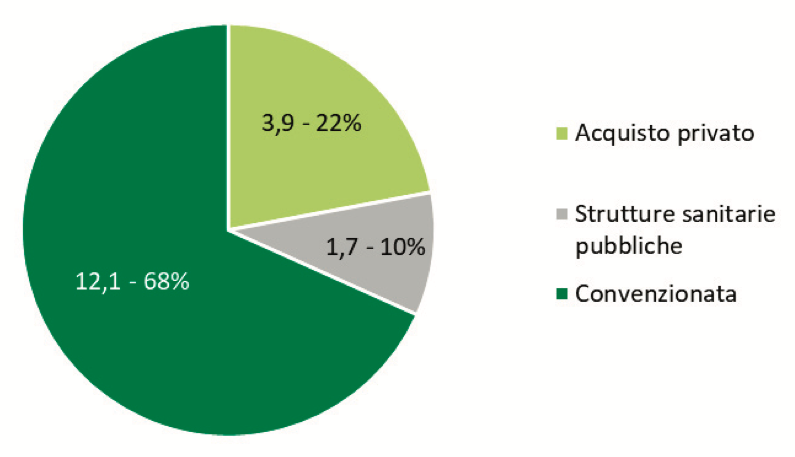 per capita expenditure of 2.05 euros.
per capita expenditure of 2.05 euros.
Approximately 90% of the consumption of antibiotics paid by the NHS (12.1 DDD/1000 inhab day) is provided under an agreed assistance regime, confirming that a large part of the use takes place following the prescription of the General Practitioner or Pediatrician of Free choice.
Penicillins in combination with beta-lactamase inhibitors are confirmed as the most consumed class, followed by macrolides and fluoroquinolones.
Compared to 2016, there was an overall reduction in the consumption of systemic antibiotics of 27.4% and the categories that contributed most to this decrease were the combinations of penicillins (including beta-lactamase inhibitors), macrolides and fluoroquinolones. However, it should be remembered that the consumption of fluoroquinolones was already in sharp decline in 2019, following the restrictions on the use of these antibiotics established by the EMA at the end of 2018 and subsequently by AIFA
AIFA -The use of antibiotics in Italy. National Report 2020